By Amnesty International
Photos: Wikimedia Commons
Some of the world’s biggest arms exporters are continuing to openly flout the rules of the Arms Trade Treaty through unlawful arms transfers, leading to a devastating loss of life in conflict zones such as the Occupied Palestinian Territory, in particular the occupied Gaza Strip, Sudan and Myanmar, said Amnesty International over ten years on from the treaty’s adoption.
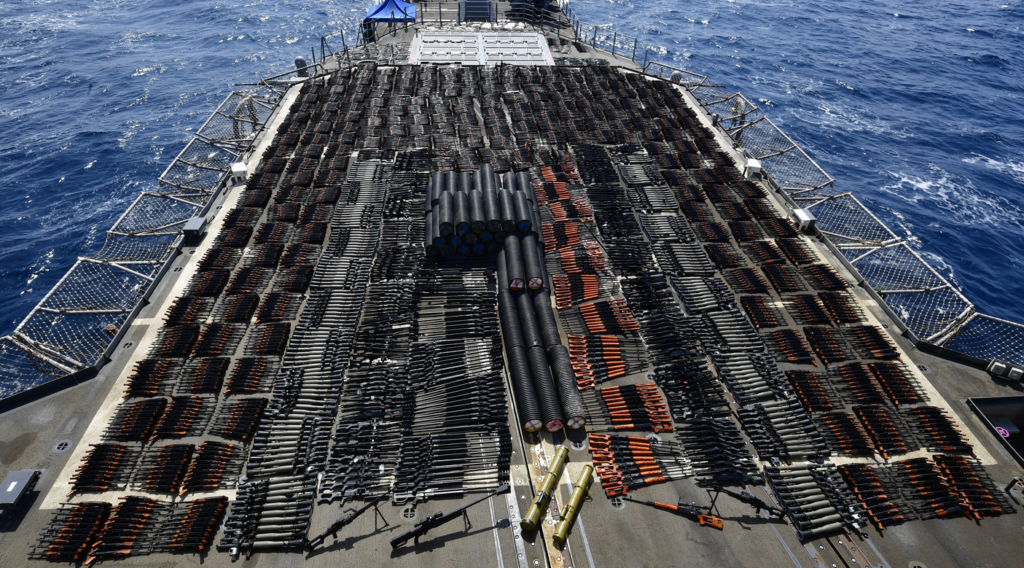

Since the Arms Trade Treaty entered into force almost a decade ago, Amnesty International has continued to document and expose unlawful arms transfers that facilitate grave abuses, contravening the robust, legally-binding, global rules on international arms transfers the treaty established. On 2 April 2013, a total of 155 states voted to adopt the Arms Trade Treaty. Today, the treaty has 115 state parties and 27 signatories, including all of the top 10 arms exporters – which account for over 90% of the arms trade – except Russia.
“The Arms Trade Treaty is the first of its kind to set global standards to govern the international trade in conventional arms and munitions. The legality of an arms transfer is now explicitly linked to international human rights and humanitarian law rules,” said Patrick Wilcken, Amnesty International’s Researcher on Military, Security and Policing.
“Although progress has been achieved, numerous governments continue to brazenly flout the rules, leading to a huge loss of life in conflict zones. It is time for state parties to live up to their legal obligations and fully implement the Arms Trade Treaty, to prohibit the flow of arms to countries when it is known they would be used for genocide, crimes against humanity, war crimes or if it could be used to commit or facilitate serious violations of international human rights or humanitarian law.”
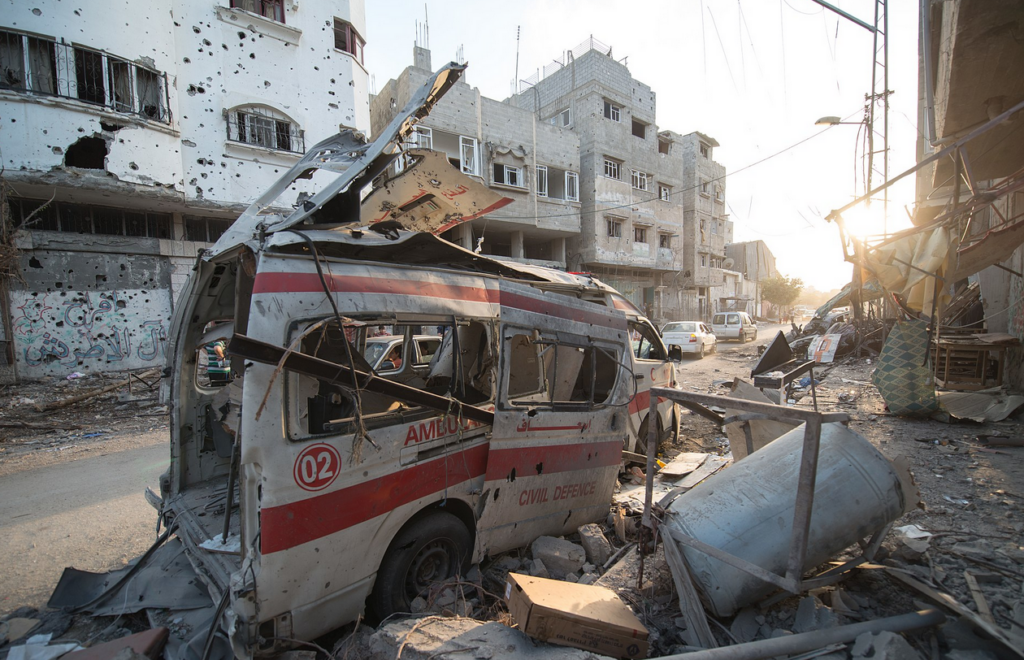

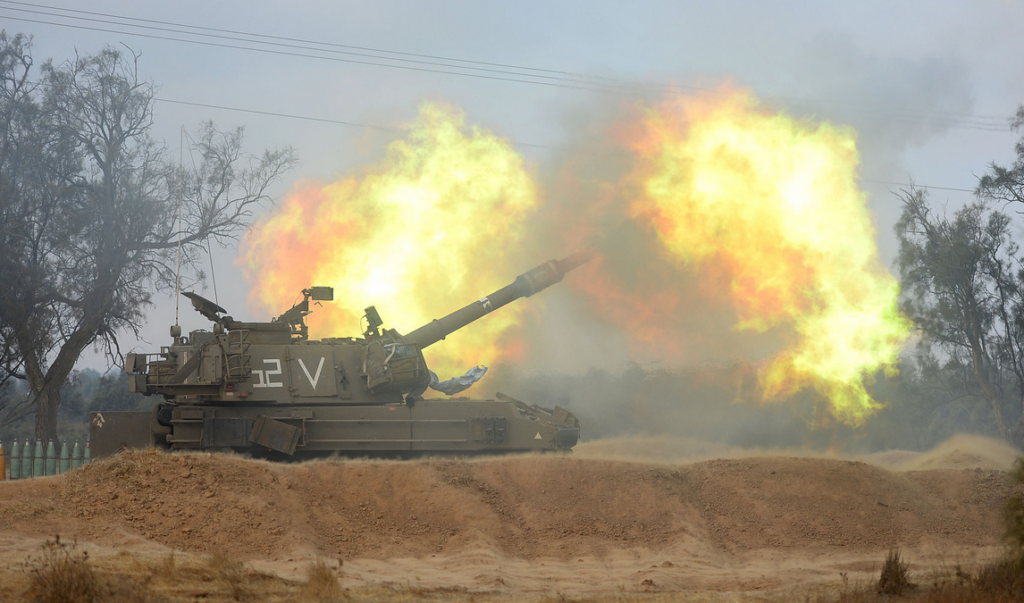
Unlawful arms transfers to Israel
The continued transfer or arms to Israel is a stark example of the failure by state parties to fully comply with the Arms Trade Treaty, or, regarding signatories, not undermine its object and purpose.
“Amnesty International has long been calling for a comprehensive arms embargo on both Israel and Palestinian armed groups because of longstanding patterns of serious violations of international human rights and humanitarian law, including war crimes, leading to horrific impacts on civilians, including women and children,” said Patrick Wilcken.
“States parties and signatories, including the USA – the largest provider of arms to Israel – continue to licence arms transfers to Israel in spite of overwhelming evidence of war crimes committed by Israeli forces.”
For example, Amnesty has documented the use of US-manufactured weapons in a number of unlawful airstrikes, including US-made Joint Direct Attack Munitions (JDAM) in two deadly, unlawful air strikes on homes in the occupied Gaza Strip, which killed 43 civilians – 19 children, 14 women and 10 men – on 10 and 22 October 2023.
A GBU-39 Small Diameter Bomb, made in the US by Boeing, was used in an Israeli strike in January 2024 which hit a family home in the Tal al-Sultan area of Rafah, killing 18 civilians, including 10 children, four men, and four women.
Illegal arms trade fuels unrest in Sudan
Illegal arms transfers have also fuelled unrest in Sudan. Since the escalation of the conflict in April 2023, Sudan has been engulfed in a massive human rights and humanitarian crisis. The fighting between the Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF) and the Rapid Support Forces (RSF) and their allies has killed more than 16,650 people and displaced millions of others, making Sudan the world’s largest internal displacement crisis.
Despite this crisis, and a UN Security Council arms embargo on the Darfur region, Amnesty International continues to document substantial flows of weapons into the conflict. Amnesty International has identified recently-manufactured weapons and military equipment from countries such as China and Serbia, who are state parties to the Arms Trade Treaty, and signatories Türkiye and the United Arab Emirates (UAE), that are being imported in large quantities into Sudan, and then in some cases diverted into Darfur, fuelling the violence.
Myanmar imports at least $1 billion USD in arms
According to the Special Rapporteur on the situation of human rights in Myanmar, the military has imported at least $1 billion USD in arms, dual-use goods, equipment, and raw materials to manufacture weapons – including from China – since it initiated a military coup in February 2021.
“The Myanmar military has used these weapons to repeatedly attack civilians and civilian objects – often destroying or damaging schools, religious buildings and other key infrastructure – in the three years since carrying out a coup,” said Patrick Wilcken.
Moving forward
Since the early 1990s, Amnesty International has been campaigning with NGO partners to achieve robust, legally binding global rules on international arms transfers to stem the flow of arms that fuel atrocities, yet more needs to be done to ensure this treaty is upheld to stop further bloodshed.
“Too many lives have been lost to these dangerous weapons. State parties and signatories to the Arms Trade Treaty cannot afford to shirk their obligations any longer,” said Patrick Wilcken. “As the Arms Trade Treaty nears the 10-year anniversary of its entry into force, states must stand true to the treaty and reduce human suffering now.”

Background information
- The 10th Conference of States Parties to the Arms Trade Treaty will be taking place on 19-23 August, where Amnesty International will be calling for a halt to arms sales to Israel.
- On 2 April 2013, a total of 155 states voted in the UN General Assembly to adopt the Arms Trade Treaty, which entered into force in December 2014.
- More than a million people around the world joined the campaign, calling on governments to agree a strong Arms Trade Treaty with robust rules to protect lives.
- According to the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI), the United States, a signatory, is responsible for 42% of the global arms trade. Some transfers made by state parties and signatories are in clear violation of the Arms Trade Treaty’s core human rights obligations and principles.
- According to Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI), overall military expenditure has increased for the ninth consecutive year in 2023, reaching a total of over US$2.4 trillion – the highest level SIPRI has ever recorded.